The uShape node is used to produce several basic primitive 3D shapes, including capsule, torus, planes, cubes, spheres, and cylinders.

uShape Node Setup
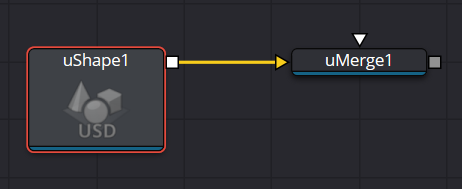
uShape Node Controls Tab
Shape
This menu allows you to select the primitive geometry produced by the Shape 3D node. The remaining controls in the Inspector change to match the selected shape.
The Shape primitives are Capsule, Cone, Cube, Cylinder, Ico sphere, Plane, Sphere and Torus.
Double Sided
This will make the polygons have two faces and receive lighting on both sides
Lock Width/Height/Depth
Only for Plane and Cube shapes. If this checkbox is selected, the width, height, and depth controls are locked together as a single size slider. Otherwise, individual controls over the size of the shape along each axis are provided.
Size Width/Height/Depth
Only for Plane and Cube shapes. Used to control the size of the shape.
Radius
When a Capsule, Sphere, Cylinder, Cone, or Torus is selected in the shape menu, this control sets the
radius of the selected shape.
Height
When a Capsule, Cone, or Cylinder is selected in the shape menu, this control sets the height of the
selected shape.
Top Radius
When a cone is selected in the Shape menu, this control is used to define a radius for the top of a
cone, making it possible to create truncated cones.
Subdivision Level/Base/Height/Cap/Cylinder
The Subdivision controls are used to determine the tessellation of the mesh on all shapes. The higher
the subdivision, the more vertices and polygons in each shape.
Subdivision Scheme
The Subdivision Scheme defines which algorithm is used to tessellate the polygons in the shapes.
The methods are None, Bilinear, Loop and Catmull-Clark.
Angle
When the Capsule, Cone, Cylinder, Sphere, or Torus shape is selected in the Shape menu, this range
control determines how much of the shape is drawn. A start angle of 180° and end angle of 360° would
only draw half of the shape.
Latitude
When a Sphere or Torus is selected in the Shape menu, this range control is used to crop or slice the
object by defining a latitudinal subsection of the object.
Cap Bottom/Top
When Cylinder or Cone is selected in the Shape menu, the Bottom Cap and Top Cap checkboxes are
used to determine if the end caps of these shapes are created or if the shape is left open
Section
When the Torus is selected in the Shape menu, Section controls the thickness of the tube making up
the torus.
uShape Node Material Tab
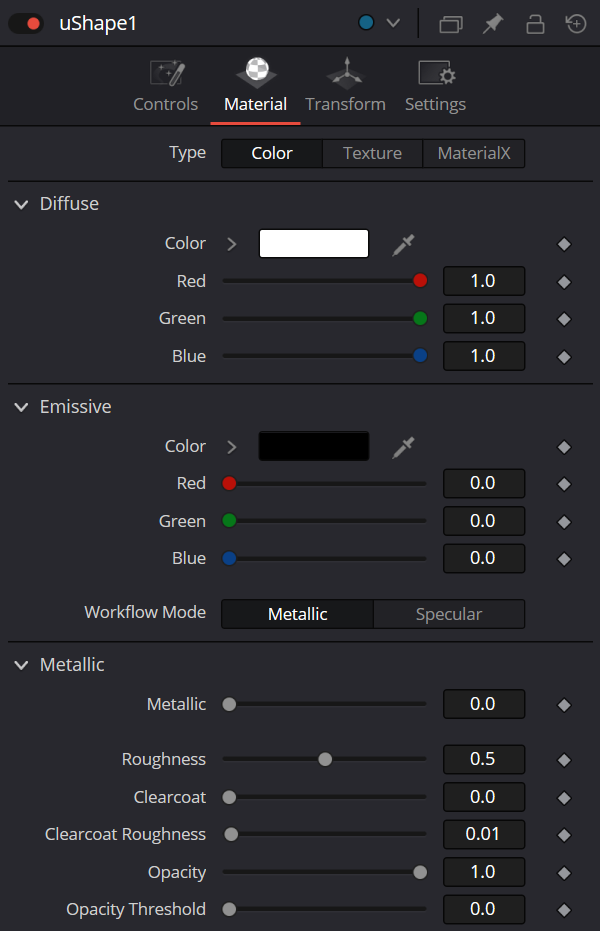
Diffuse Mode
Diffuse describes the base surface characteristics without any additional effects like reflections or
specular highlights.
- Color: Provides controls to modify the shape’s diffuse color.
- Texture: This control allows you to use a source image as the diffuse surface color. Use the Browse button to open the file browser and select an image file.
Emissive
Emissive adds a global lighting effect to a shape, creating a layer of color over the existing texture.
It can be adjusted to different levels of intensity and can be used to simulate the emission of light.
Workflow Mode
Lets you set the mode between Metallic and Specular.
- Metallic: When enabled, this control shows the Metallic slider. The Metallic slider adds a reflective quality to objects, creating the appearance of metal. It enhances the reflective properties of a shape.
- Specular: When enabled, this shows the Specular Color controls. Specular Color determines the color of light that reflects from a shiny surface. The more specular a material is, the glossier it appears.
Roughness
Affects the amount of light reflection and scattering on a surface, giving it a smoother or more textured appearance depending on the setting. It is a key element in creating realistic reflections.
Clearcoat
Affects the appearance of a surface by adding a glossy layer on top of it, mimicking the effect of a protective coating. It is commonly used in creating materials like car paint or polished metal.
Clearcoat Roughness
Adjusts the level of imperfection or smoothness of the glossy layer added on top of a surface. This can affect the realism and reflection of materials like car paint or polished metal.
Opacity
Reduces the material and object opacity, impacting the color and Alpha values of the shape.
Common Controls
The Transform and Settings tab in the Inspector is also duplicated in other USD nodes.


