The Channel Boolean (not to be confused with the 2D Channel Booleans) can be used to remap and modify channels of 3D materials using mathematical operations. For example, if you want to use the red channel of a material to control a scalar input of an illumination model that uses the Alpha channel (e.g., Blinn. SpecularExponent), you can remap the channels here. Furthermore, it allows the use of geometryspecific information like texture space coordinates and normals.
Channel Boolean Node Inputs
There are two inputs on the Channel Boolean Node: one for the foreground material, and one for the background material. Both inputs accept either a 2D image or a 3D material like Blinn, Cook-Torrence, or Phong node.
- BackgroundMaterial: The orange background material input accepts a 2D image or a 3D material.
- ForegroundMaterial: The green foreground input also accepts a 2D image or a 3D material.
Channel Boolean Node Setup
There are many uses for the material 3D Channel Boolean. Most often it is used to combine material looks or manipulate UV texture coordinates
In the below example, the Channel Boolean node combines the Cook Torrance and Blinn materials. It uses the math operands in the Channel Boolean to switch, invert, and mix the two inputs, creating a neon flickering effect.
Channel Boolean Node Controls Tab
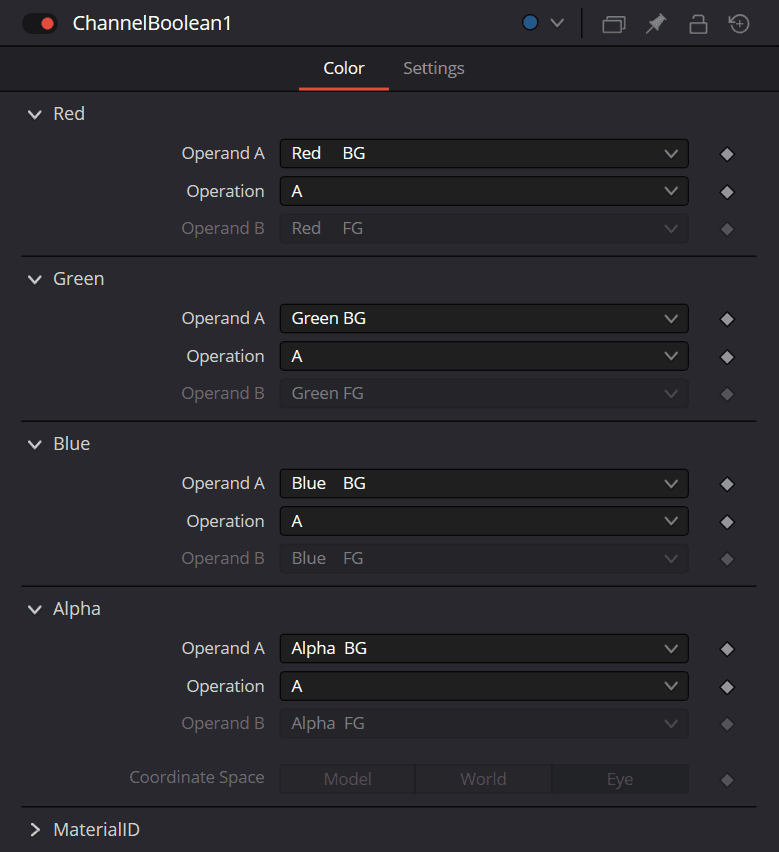
The Controls tab includes a section for each RGBA channel. Within each channel are two input menus called Operand A and Operand B. The function performed on these two inputs is selected in the Operation menu.
Channel Boolean Operand A/B
The Operand menus, one for each output RGBA channel, allow you to set the desired input information for the corresponding channel.
- Red/Green/Blue/Alpha FG
Reads the color information of the foreground material. - Red/Green/Blue/Alpha BG
Reads the color information of the background material. - Black/White/Mid Gray
Sets the value of the channel to 0, 0.5, or 1. - Hue/Lightness/Saturation FG
Reads the color information of the foreground material, converts it into the HLS color space, and puts the selected information into the corresponding channel. - Hue/Lightness/Saturation BG
Reads the color information of the background material, converts it into the HLS color space, and puts the selected information into the corresponding channel. - Luminance FG
Reads the color information of the foreground material and calculates the luminance value for the channel. - Luminance BG
Reads the color information of the background material and calculates the luminance value for the channel. - X/Y/Z Position FG
Sets the value of the channel to the position of the pixel in 3D space. The vector information is returned in eye space. - U/V/W Texture FG
Applies the texture space coordinates of the foreground material to the channels. - U/V/W EnvCoords FG
Applies the environment texture space coordinates to the channels. Use it upstream of nodes modifying the environment texture coordinates like the Reflect 3D node. - X/Y/Z Normal
Sets the value of the channel to the selected axis of the normal vector. The vector is returned in eye space.
Channel Boolean Operation
Determines the Operation of how the operands are combined.
- A: Uses Operand A only for the output channel.
- B: Uses Operand B only for the output channel.
- 1-A: Subtracts the value of Operand A from 1.
- 1-B: Subtracts the value of Operand B from 1.
- A+B: Adds the value of Operand A and B.
- A-B: Subtracts the value of Operand B from A.
- A*B: Multiplies the value of both Operands.
- A/B: Divides the value of Operand B from A.
- min(A,B): Compares the values of Operands A and B and returns the smaller one.
- max(A,B): Compares the values of Operands A and B and returns the bigger one.
- avg(A,B): Returns the average value of both Operands.
Material ID
This slider sets the numeric identifier assigned to this material. This value is rendered into the MatID auxiliary channel if the corresponding option is enabled in the renderer.
Channel Boolean Node Settings Tab
The Settings tab in the Inspector is duplicated in other 3D nodes. These common controls are described in detail HERE.


